Dave Ulrich: Creating a multi-generational playbook to engage employees
- 4 Min Read
HR thought leader Dave Ulrich explores how leaders can get the most out of those they lead by finding commonality and appreciating differences.
- Author: Dave Ulrich
- Date published: Oct 10, 2022
- Categories

Leading others is a subtle art. It requires connecting around common values to build mutual understanding while also appreciating differences to personalize a relationship. Effective business and HR leaders get the most out of those they lead by finding commonality about why people work and appreciating differences (like generations, gender, race, ethnicity, education, geography, age, body type, personality style, and so forth) about how people work to help employees achieve their full potential. The art of finding common values and unique behaviors can be illustrated by examining workforce generations.
Multi-generational workforce
In almost every management conference and popular press on the workforce, we are reminded how different generations approach work: baby boomers (1946 to 1964), Gen X (1964 to 1980), Gen Y or Millennials (1981 to 1996), and Gen Z (after 1997). A summary of these perceived generational differences are in figure 1.
Figure 1: Perceived generational differences
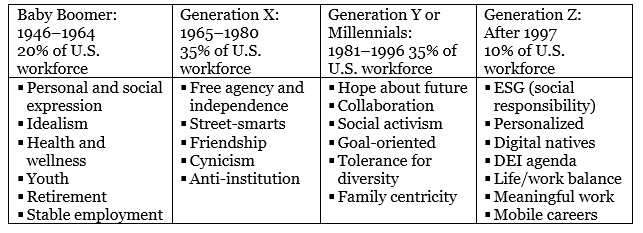
Note that the U.S. workforce percentages would not be the same as other countries where demographics percentages may differ, but the four generations still exist.
While recognizing generations of employees is interesting, we must separate why people work from how they work to fully understand multi-generational approaches to work. Knowing why people work explains underlying motives and helps us forge common bonds across generations. Understanding how people work explains current behaviors and helps us tailor management approaches for each generation.
Why People Work
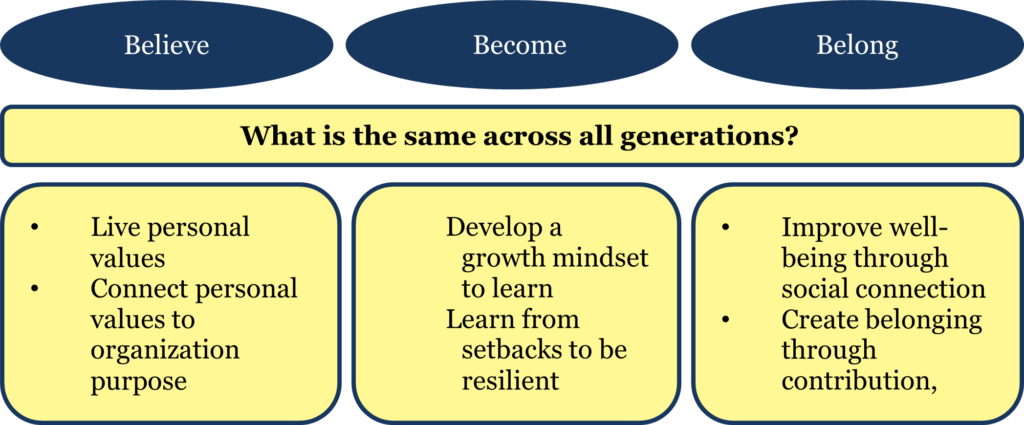
Knowing why people work is about determining motivations for work and shaping an employee experience at work. When asked to divide 100 points across ten motives for work, each generation divides the points about equally. In our summary of why people work, we found seven common drivers that apply equally across generations identity, purpose, work environment, work itself, relationships, learning, and delight. We have since clustered these seven dimensions into three drivers of employee experience (see figure 2):
- Believe: Finding meaning and purpose from work.
- Become: Learning and growing from work.
- Belong: Building relationships and connections at work.
These three drivers of employee experience are shared across generations: people are people. While some propose that next-generation employees’ altruistic values are changing society, those of us who are baby boomers remember that we also changed education, housing, and work. All generations want to do work that makes a difference in the world and make it better. Leaders who understand these common motives can better relate to employees across generations.
Figure 2: Drivers of employee experience
How People Work
How people work is about work expectations and style based on many demographic and personal dimensions. An overview “how” each generation approaches work is in figure 3.
Figure 3: How generations approach work
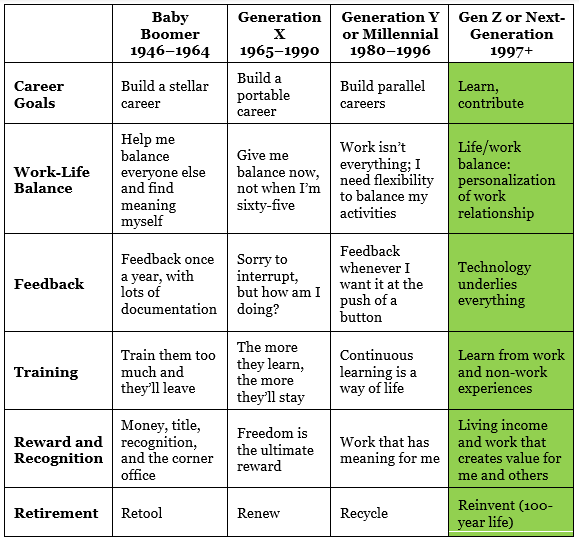
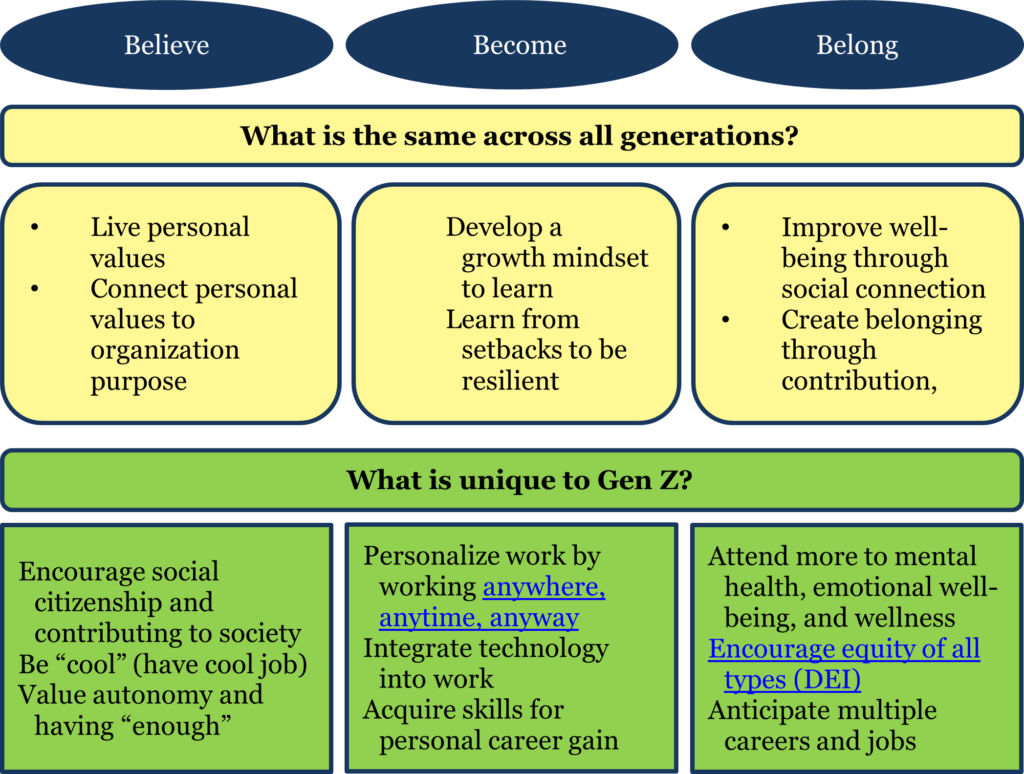
Each generation has some unique work processes. Since Gen Z workers are expected to more than triple to 87 million people by 2030 (in the United States) accounting for 30 percent of total employment, exploring their uniqueness is helpful. At the risk of over simplifying a complex phenomenon and recognizing a lot of variance within each generation, we see unique ways that Gen Z lives the fundamental principles of believe, become, and belong (see figure 4).
- Believe: Gen Z workers are driven ever more by social citizenship. “Doing well by doing good” is often a mantra Gen Z strives to use to be socially responsible to the environment and world. Donating time and money to social causes is often a priority. In a world of frequent mistrust, Gen Z seeks to affiliate with organizations where it can experience trust through shared purpose.
- Become: Gen Z seeks to learn and to grow. Having “flexible” work practices is not enough: work practices must be personalized. Personalization means caring for the “person” as well as shaping tailored and customized policies, often through technology, to the unique needs of an employee, which may mean where and how work is done.
- Belong: Gen Z feels a need to attend to their personal connections but also social connections through social initiatives like DEI, attention to mental health and emotional well-being, and work relationships across companies. While all generations have some of these characteristics, leaders who appreciate these life and work style differences can adapt work requirements to individual employees.
The value of combining what is shared across generations (why people work and drivers of employee experience) and what is unique within a generation (how people work and work assumptions) is in leaders having a set of shared beliefs tailored to the specific needs of individual employees.
Figure 4: What is the same across generations and what is unique to Gen Z
Implications of Generational Work
Effective business and HR leaders enable others by finding commonality about why people work and appreciating generational (and other) differences about how people work to help employees achieve their full potential. This combination leads to the personalization of today’s workforce.









